
Extensive research has been conducted with regard to the overwhelming health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 appears to play a role in a wide range of conditions, from asthma to heart disease.
The body cannot produce these important polyunsaturated fats on its own. They must be acquired daily through a healthy diet or supplementation.
The 3 Omegas:
There are 3 forms of omega-3 fats:
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
Of these 3, DHA and EPA are the most beneficial to our health. The body partially converts ALA into eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Many human diseases, including heart disease and diabetes, have been linked to inflammation. Generally, some omega-6 fatty acids promote inflammation, whereas omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties. Here’s how:
Inflammation is an important mechanism. It prevents an infection from spreading to nearby tissues and organs. If the inflammatory process continues, however, it can damage nearby tissues and organs.
When an infection is present, the immune system triggers the production of prostaglandins, which are fatty acid compounds with hormone-like effects.
| Prostaglandin 1: Anti-inflammatory (suppresses the inflammatory response)
Prostaglandin 2: Inflammatory (triggers the inflammatory response) |
The prostaglandin known as Prostaglandin II triggers an inflammatory response, sending white blood cells to the infected area to quarantine the infection. Almost immediately, the immune system triggers the production of Prostaglandin I to suppress inflammation and begin the healing process.
In other words, omega-3 helps to shut down the inflammatory response, preventing chronic inflammation.
This infographic explains how the conversion of omega-6 and omega-3 promotes or reduces inflammation:
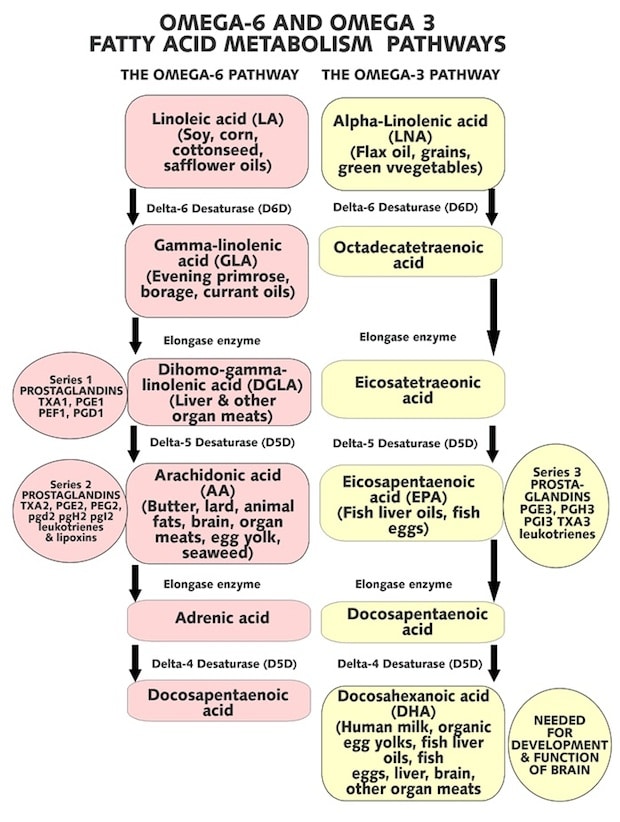
Source: becomehealthynow.com/popups/fatty_acids_bh.htm
Because of their role in suppressing the inflammatory response, omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) have been shown to benefit these conditions:
Arthritis
The powerful anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 help reduce stiffness in joints and help relieve joint and muscle pain.
Brain Health
Approximately 50 percent of the make-up of the human brain is DHA. DHA promotes good mental health by reducing the risk of depression, ADHD, helping to increase focus and memory retention in children and adults. Omega-3 also supports healthy neurological development in infants.
Cardiovascular Disease
Omega-3 helps reduce ‘bad’ cholesterol (LDL) levels and triglycerides and raise ‘good’ cholesterol (HDL) levels.
Depression and Mood Regulation
Regular supplementation with omega-3 can elevate mood and reduce depression and anxiety. High-potency fish oil with added Vitamin D is useful for treating Seasonal Affective Disorder or the “winter blues”.
Vision Problems
Omega-3 reduces the risk of age-related vision problems including macular degeneration. The DHA found in fish oil is important for an infant’s visual development.
Skin Conditions
Omega-3 is the ultimate skin food. It helps maintain healthy cell membranes, producing softer, more youthful skin. Omega-3 also helps to reduce inflammatory compounds that promote aging and skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Regular omega-3 supplementation helps to soothe and lubricate the bowel, ease elimination, and support overall digestive health. Fish oil is helpful in treating many gastrointestinal disorders such as ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and inflammatory bowel disease including Crohn’s Disease and colitis.
Breast Cancer & Prostate Cancer
A 2013 study found that omega-3 helps to stop or slow the proliferation of certain types of breast cancer cells. Population-based studies of groups of men suggest that a low-fat diet that includes omega-3 helps prevent the development of prostate cancer.
Oil Change
Modern diets provide an overabundance of omega-6 fatty acids, mostly from refined vegetable oils (soybean, corn, cottonseed, and safflower oils) that are used to fry food as well as snack foods, cookies, and crackers. Conversely, omega-3 has become relatively rare in American diets. The result is an imbalance of these essential fats – promoting inflammation and disease.
| Oil | Omega-6 Content | Omega-3 Content |
| Safflower | 75% | 0% |
| Sunflower | 65% | 0% |
| Corn | 54% | 0% |
| Cottonseed | 50% | 0% |
| Sesame | 42% | 0% |
| Peanut | 32% | 0% |
| Soybean | 51% | 7% |
| Canola | 20% | 9% |
| Walnut | 52% | 10% |
| Flaxseed | 14% | 57% |
| Fish | 0% | 100% |
Reference: chriskresser.com/how-too-much-omega-6-and-not-enough-omega-3-is-making-us-sick
The best food sources of omega-3 fatty acids are:
|
|
These foods contain omega-3 and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA):
|
|
As you can see, although some of these foods are commonplace in a healthy diet, many people are not reaching the 1,000 mg daily minimum recommended by most health experts – and that amount is just for maintenance. For chronic inflammation, 2,000 to 4,000 mg is recommended.
Many people avoid fish due to environmental toxins such as mercury, PCBs, and pesticides, but don’t skip out on omega-3 just because of the risk. Safe seafood that is high in nutrients, low in toxins, and farmed or caught sustainably is available, often at your local supermarket. The website, GreenAmerica.Org provides a ‘Safe, Sustainable Seafood Guide’. Refer to this list often for updates.
Supplementing with high-quality fish oil provides omega-3 health protection in a purified form without environmental toxins. Fish oil supplements vary in the amounts and ratios of DHA and EPA they contain. For example, salmon oil naturally contains more DHA than EPA and a supplement derived from algae may only contain DHA. Krill oil contains significant amounts of both EPA and DHA. So, which omega-3 supplements should you reach for? Based on your current health concerns and diet preferences, you can determine which supplement best suits your needs.
Here is a simple guideline to follow: If your main priority is mental health, look for a supplement that provides more DHA. If pain and inflammation are your top concern, purchase a product that has more EPA than DHA.
Fish oil
Fish oil is, by far, the most popular omega-3 supplement, especially since many are concerned about the safety of eating fish. Most fish oil brands provide a combination (and healthy balance) of DHA and EPA.
Krill oil
Research indicates your body can absorb the omega fatty acids in krill oil more easily than it can from fish oil or plants. Krill oil also provides vitamin E, vitamin A, and vitamin D.
Cod liver oil
Cod liver oil provides omega-3 as well as vitamins A and D. Many people choose to take cod liver oil supplements during the winter months when natural sunlight and vitamin D are in short supply. Cod liver oil often contains a lower concentration of omega-3 when compared to krill oil and other fish oil supplements.
Vegetarian omega-3 supplements
Flaxseed oil contains alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which the body converts into EPA and DHA. Researchers suggest that the body is not very efficient at converting ALA into EPA and DHA, but some supplement companies, such as Barlean’s, are finding ways to ‘pre-convert’ ALA to EPA and DHA in their plant-based omega-3 supplements. Borage oil
Algae-based supplements (microalgae) that are rich in DHA and EPA are now widely available. This is an excellent option for vegans and for those concerned with the environmental pollutants that accumulate in fish oil.
Read more about vegetarians and omega-3 fats
How much should you take?
Omega-3 fatty acids are beneficial for adults and children. The dosages vary for different age groups:
- Children aged 5 to 14 years – 500 mg a day
- Healthy adults under the age of 40 – 1000 mg a day
- Adults over the age of 40 with a high risk of heart disease, arthritis, or other inflammatory conditions – 2,000 mg a day
- Cod liver oil should not be taken in doses above 2000 mg due to its vitamin A content. Vitamin A can be toxic when taken in large doses.
Your healthcare practitioner can help you determine the omega-3 amount best suited for you.
Cautions & Contraindications
Omega-3 is an effective blood thinner, so individuals with a history of bleeding disorders (thrombocytopenia, hemophilia, coagulation factor deficiency, or other conditions) and those taking prescription blood thinners such as Coumadin, Warfarin, and Plavix, or over-the-counter aspirin should consult a physician prior to taking omega-3 supplements.
As a precaution, also check with your doctor before taking omega-3 if you are currently being treated with any of the following medications: diabetes medications; cyclosporine; etretinate; and topical steroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Your challenge is to include more omega-3 sources in your diet. Here is a reminder of how to do it:
- Eat an omega-3-rich fish at least twice a week.
- Add chia seeds, hemp seeds, or ground flaxseed to your smoothies, salads, yogurt, cereals, and baked goods, and find other creative
- ways to incorporate them.
- Nosh on nuts, specifically walnuts, and sprinkle a few over a salad (which includes kale or spinach leaves).
- Take a supplement containing EPA/DHA daily.
Image: Veganbaking.net




